Planning Poker In Agile Methodology
What is Planning Poker®? Agile development teams complete work in sprints, typically 2-3 week periods during which a team works exclusively on an itemized to-do list known as a sprint backlog. During sprint planning, teams work together to estimate the level of effort required for development of each upcoming backlog item (also called user stories) through a process called effort pointing. What is Planning Poker in Agile? In simple words, it is a game used to estimate the efforts and hence find the product backlogs. It is consensus-based and used to estimate the user story size in a scrum.
We are glad that you have started working on agile projects. You are performing great in stand up meetings and planning for sprints. Your retrospectives are working just fine. In short, you are delivering your product to the end-user as expected. However, these are wishes all of us have when we work on projects. But there are pitfalls and don’t worry as they can be handled with the help of proper planning and estimation techniques. Yes, that is where we talk about the scrum poker. Does it look like a new word? Then call it planning poker that is how it is popularly known to the people in the agile world. We also call it pointing poker.
In this blog, we would want to provide you with all the details about Agile planning poker and the right way to use this estimation tool to execute your sprints per the plan devised.
What is Planning Poker in Agile?
In simple words, it is a game used to estimate the efforts and hence find the product backlogs. It is consensus-based and used to estimate the user story size in a scrum. A decade before in 2002 James Grenning named this game as estimation poker after some time officially Mike Cohn made this technique popular through his Agile book. He also created planningpoker.com allowing people to play for free and make the best use of the tool.
Best time to employ Planning Poker?
Before starting get an idea about absolute and relative estimation as well as point vs man-hour estimation that will make you understand the need for planning poker agile. Basically, we engage in planning poker as it is a size estimation technique.
Do we have to use this technique after writing the first product backlog? According to us, the answer is no. Can you guess why? It is because, we are well aware that poker planning is a size estimation technique and if it is done just after writing the first product backlog, then there will be additions of user stories which will lead to estimates again. Therefore we suggest using planning poker at the end of every iteration. This will save time and re-estimation efforts as well. It is better to do this in few days prior to the completion of iteration and then follow it up with a daily standup. This will allow the entire team to participate.
Poker planning and distributed team
Planning poker online tool was offered to the world by Mike Cohn. This can be used by distributed teams and thus it is greatly promoted by the agile coach and trainers to all people in the agile community.
Scrum poker online tool fosters teamwork as it engages all the team members from the distributed team. It makes an estimate in consensus and not just one person drives the estimate. The issues are highlighted well in advance for every story point by allowing the team to discuss constructively. A distributed team is basically a team that is located in a different location. So it is now easy for all teams to connect with this one tool.
Agile Estimation – Relative Vs Absolute
The very word estimation in simple English is guessing. With experience and knowledge senior people in the team estimate the time required to complete any particular work. In case, if you are new to the work, then what experience you will have? How can you guess the time or plan a work? Then you need some references and they can be obtained from the previous works. For this, you don’t need experience. We can always quickly relate and come to a conclusion.
Therefore understand relative vs absolute like this. Relative is to compare with and absolute is beyond comparison defined theoretically which is the actual. You cannot be rigid and define a time frame as absolute cannot be possible always. Relative can happen by comparing several past work and estimate on the time and efforts.
I call relative as arbitrary and absolute as real. Not everything is possible in reality and thus absolute may or may not happen. On the other hand, relatives can always be fine-tuned and attain closer to accuracy.
| S.No | Relative Estimation | Absolute Estimation |
| 1 | Comparison is done and there is no room for isolated estimation. | The means estimation is done and there is only item isolation but no comparison |
| 2 | Relative value | Absolute value |
| 3 | Value is decided upon comparing with another value | It is decided one time and there is no comparison |
| 4 | No tools to measure but an arbitrary value | Measured using tools and accurate |
| 5 | May or may not be accurate | Accurate |
Point vs Hour Value in Estimation
Is it a good estimate with hour value or story points? Let us understand the difference between both to conclude the best technique.
| Story points | Hours Value |
| Time taken to complete each user story is measured | Time taken by the individual and team in completing an action is the hour's value. |
| Experience or skill of the estimator is not correlated | Based on the skills and experience only the time varies |
| Velocity is tracked | Velocity is not tracked |
| No re-estimation is required | Re-estimation is needed when man-hour is estimated as it tends to change based on the time and person who completes a task |
What is planning poker estimation - Tips for using planning estimate effectively?
It is an estimation technique and a discrete scaling method. It is played using the cards that are represented as modified Fibonacci series.
Lets us explain with an example. When a task requires 2 weeks for completion, then the estimator will choose either a card with 13 or 20. Each estimator will open their cards and come to consent on one card either 13 or 20 and work towards achieving the goal.
We suggest you split the user stories for more effective estimation. Use the “?” card and gather information before choosing the right card.
Wall map the stories by taking the smallest story as a reference which can be coded and tested in one day. Arrange the stories from left to right and split the bigger story into small to estimate them effectively. Choose only relevant cards and ignore estimates that are high and reveal false accuracy.
When to use?
Use this game for effective estimation and start at the zero sprints which are the release estimation planning. Here you can construct the estimates for each feature request which is called a task in simple words. This will size the project. Also, use it during the estimation of the new story to recognize the iteration process.
Who should participate in planning poker in scrum?
The product owner or the analyst who plays the role of a moderator is the key player in the planning poker estimation technique.
Next comes the estimators who participate to select the cards and check them to come to a final consent. These estimators include the developers, database engineers, testing engineers, and user interface designers. Basically, this tells you that all involved in the agile project needs to be an active participant to plan using the poker cards.
Planning Poker – Does it work? Yes, follow these tips
We believe that it is the best estimating technique and accurate too. Planning poker estimation technique helps to bring the collective opinion of different experts from all cross-functional team. Therefore, the estimate is done from a different perspective and thus looks perfect.
1. Do a detailed review of the software literature is done before estimation.
2. It works effectively is estimated by the competent team.
3. Engage in a lively discussion with the team and the estimator should involve their peers and confirm their estimates. This will enhance the accuracy of the items with uncertainty.
4. All missing information is collected to justify the estimates
5. Average every single estimate and then planning to estimate for the best results.
Order Planning Poker cards?
Before you order for planning poker cards, know them.

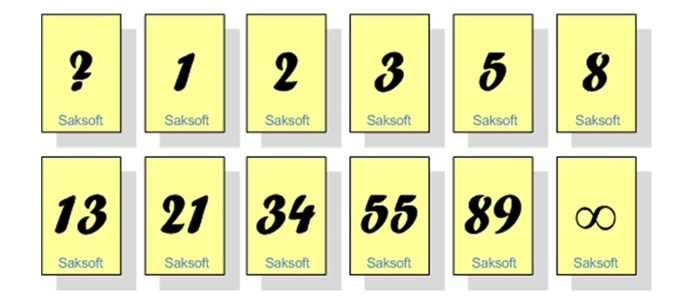
Figure 1: Planning poker cards
• These are the deck of cards and each deck contains 4 sets of cards namely the 0, ½, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20, 40, 100…. You guessed it correct, it is Fibonacci series with slight modifications.
• Zero cards confirm that the story is completed; it may also be not a worthy one to be discussed. For either situation, it is marked as zero.
• The card that is a ? will confirm that the estimator is clueless about the task.
• There is a coffee cup that indicates a need for a break.
Now, know that these scrum poker cards are available online in Amazon for sale. The brands include Bee, Bicycle, or World Poker Tour cards.
How does planning poker work – Steps in detail
This is an agile planning poker scrum activity. Every estimator will have a deck of cards and begin with the exercise.
Figure 2: Steps involved in a planning poker game
The participants are the moderators in the scrum poker. The session initiator in the agile poker is the moderator who can cancel any item estimated and choose per their wish. The final result can be edited by this person and also allow voting to restart the item.
1. First, the moderator will read the details. This is usually the product owner and he does it for every user story/theme which needs estimation.
2. Then the discussion starts and the PO will address the answers for the estimator’s questions. The goal to be kept in mind is not to arrive at an estimate but make a value estimate in a cost-effective manner.
3. Now the estimators will individually select the card based on the discussion to represent their estimation. After the selection is completed by all individuals, everyone will simultaneously turn the card to reveal their estimate to all participants. Don’t expect them to be the same and they will differ.
4. The extremely different estimates require explanation by the estimators. If required a re-estimation is done. This process is repeated until the team comes in consent with one estimate to be implemented for a particular user story.
Conclusion
In summary, planning poker estimation is the best method used to not only estimate the ideal time for task completion but also allows the team to correlate the user story properly. But, remember to bring the team to consent for each estimate. Have a healthy discussion but don’t dilute the details. Avoid using a coffee cup card often to prevent monotony in the process.
Finally, we would like to reiterate that this is an effective technique used to estimate the time taken to complete each user story. It is an influential technique too.
To understand more about planning and estimation attend StarAgile Certified Scrum Master training, for upcoming schedules please call us at +91 – 80502 05233
What is Planning Poker?
Planning Poker is an agile estimating and planning technique that is consensus based. To start a poker planning session, the product owner or customer reads an agile user story or describes a feature to the estimators.
Each estimator is holding a deck of Planning Poker cards with values like 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 20, 40 and 100, which is the sequence we recommend. The values represent the number of story points, ideal days, or other units in which the team estimates.
The estimators discuss the feature, asking questions of the product owner as needed. When the feature has been fully discussed, each estimator privately selects one card to represent his or her estimate. All cards are then revealed at the same time.
If all estimators selected the same value, that becomes the estimate. If not, the estimators discuss their estimates. The high and low estimators should especially share their reasons. After further discussion, each estimator reselects an estimate card, and all cards are again revealed at the same time.
The poker planning process is repeated until consensus is achieved or until the estimators decide that agile estimating and planning of a particular item needs to be deferred until additional information can be acquired.
When should we engage in Planning Poker?
Most teams will hold a Planning Poker session shortly after an initial product backlog is written. This session (which may be spread over multiple days) is used to create initial estimates useful in scoping or sizing the project.
Because product backlog items (usually in the form of user stories) will continue to be added throughout the project, most teams will find it helpful to conduct subsequent agile estimating and planning sessions once per iteration. Usually this is done a few days before the end of the iteration and immediately following a daily standup, since the whole team is together at that time anyway.
How does poker planning work with a distributed team?
Simple: go to PlanningPoker.com. Mountain Goat Software helped develop that website to offer it as a free resource to the agile community. A product owner, ScrumMaster or agile coach can log in and preload a set of items to be estimated. A private URL can then be shared with estimators who log in and join a conference call or Skype session. Agile estimating and planning then proceeds as it would in person.
Does Planning Poker work?
Absolutely. Teams estimating with Planning Poker consistently report that they arrive at more accurate estimates than with any technique they'd used before.
One reason Planning Poker leads to better estimates is because it brings together multiple expert opinions. Because these experts form a cross-functional team from all disciplines on a software project, they are better suited to the estimation task than anyone else.
After completing a thorough review of the literature on software estimation, Magne Jørgensen, Ph.D., of the Simula Research Lab concluded that “the people most competent in solving the task should estimate it.”
Second, a lively dialogue ensues during poker planning, and estimators are called upon by their peers to justify their estimates. Researchers have found that this improves estimate accuracy, especially on items with a lot of uncertainty as we find on most software projects.
Further, being asked to justify estimates has also been shown to result in estimates that better compensate for missing information. This is important on an agile project because the user stories being estimated are often intentionally vague.
Additionally, studies have shown that averaging individual estimates during agile estimating and planning leads to better results as do group discussions of estimates.
How can I get Planning Poker cards?
Planning Poker cards are available in the Mountain Goat Software store. Mountain Goat Software's branded Planning Poker cards are sold at cost as a courtesy to the agile community.
Our full-color cards are the absolute highest-quality cards available anywhere. They are manufactured by the same company that prints many of the world's most popular playing card brands, including Bicycle, Bee, and the World Poker Tour.
Planning Poker Agile Online
We also offer royalty-free licenses to organizations that wish to produce their own cards. The license is available here: https://www.mountaingoatsoftware.com/agile/planning-poker/license
Recommended Resources Related To Planning Poker
- How Can We Get the Best Estimates of Story Size?
- The Best Way to Establish a Baseline When Playing Planning Poker
- Don’t Average During Planning Poker
- Agile Estimating
Courses Related To Planning Poker
Agile Poker Cards
Scrum Foundations Video Series

Agile Point Poker
All the foundational knowledge of Scrum including: the framework, values, different roles, meetings, backlogs, and improving efficiency & quality.